Sign up for Lesson Plans, discounts & more!
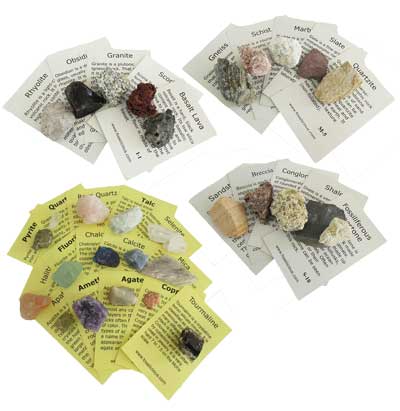
Igneous Rock Formation
Recycling Metamorphic Rocks

Igneous rock formation can happen when Metamorphic rocks are remelted. This takes place at subduction zones. Subduction zones occur when one of the earth's plates moves under another. Any metamorphic rocks sitting atop the subducting plate is pulled down. Tremendous heat is generated as the two plates grind against each other. This heat and the heat of the underlying magma melts the rock.
Volcanoes are usually present along subduction zones. They allow the heat and energy created by the grinding plates to escape to the surface of the earth.
When the magma reaches the surface through volcanoes it cools quickly, a matter of days or weeks.When the magma forms pockets underground it cools much more slowly. This could take thousands or even millions of years.
The rate at which the magma cools determines the kind of igneous rocks that are formed. Faster cooling surface lava creates rock that is fine grained or aphanitic. The rapid cooling doesn’t allow large crystals to form. I addition most of the gasses are driven off into the atmosphere.
The slower cooling that takes place underground allows larger crystal formation. Granite is an example of this type of rock formation.
Other igneous rocks are pumice, scoria, gabbro, basalt, ryolite, dacite, andesite and obsidian.
Click here for more on igneous rock formation

INTERESTED IN MORE? IF SO, YOU MAY WANT TO CHECK OUT OUR OTHER SITES:
fossilicious.com - Our online fossil and mineral rock shop.
fossils-facts-and-finds.com - An educational site about fossils.