Sign up for Lesson Plans, discounts & more!
Ruby
Ruby is a red corundum mineral with a chemical formula A2O3 aluminum oxide with chromium. It is the chromium that give rubies their red color. It is a very hard mineral, a 9 on the mohs scale. Only diamonds are harder at a 10. The word ruby comes from ruber, Latin for red. Other varieties of corundum are called sapphires.Rubies are usually found in flat hexagonal crystals.
The value of rubies is based on their clarity and color. The most desirable color is a deep blood red. They can range in color from lighter pinks to red sometimes having a less desirable brownish hue. Large clear rubies can be worth millions!
Rubies are the most valuable and popular red gemstone. They are used in all types of jewelry and traditionally has been used to decorate highly valued objects like crowns, thrones, and scabbards.
Rubies, those dazzling gemstones that ignite our imagination with their fiery red brilliance, have a captivating story rooted in science and nature. Buckle up as we venture into the exhilarating world of rubies and uncover the secrets behind their mesmerizing allure.
Formed deep within the Earth's crust, rubies belong to the mineral family known as corundum, which also includes sapphires. It's the chemical element chromium that gives rubies their vibrant red hue. The more chromium present in the crystal structure, the more intense and desirable the red color becomes. It's all about chemistry here!
Interestingly, the conditions required for ruby formation are extremely specific. They occur in the presence of igneous or metamorphic rocks combined with high pressure and temperature. These intense geological processes create the perfect environment for the birth of these magnificent gemstones.
Rubies have an impressive hardness of 9 on the Mohs scale, second only to diamonds. This property makes them incredibly durable and resistant to scratches, making them perfect for jewelry that withstands the test of time and daily wear.
In addition to their captivating color and durability, rubies also possess the unique property of fluorescence. When exposed to ultraviolet light, some rubies emit a soft glow, adding an enchanting element to their already mesmerizing allure. This phenomenon, known as red fluorescence, is highly sought after and adds an extra layer of beauty to these extraordinary gemstones.
Ruby deposits can be found in various parts of the world, with some of the most renowned sources being Myanmar (formerly Burma), Thailand, Sri Lanka, and certain regions in Africa. Each location produces rubies with slightly different characteristics, such as variations in color, clarity, and size. This natural diversity adds to the allure and uniqueness of these gemstones, making each ruby a true one-of-a-kind treasure.
Rubies have long been associated with royalty and nobility. Throughout history, they have adorned the crowns, scepters, and jewelry of kings and queens, symbolizing power, wealth, and prestige. The allure of rubies continues today, with celebrities and fashion icons often choosing these vibrant gemstones to make a bold statement on the red carpet.
Delving into the realm of metaphysics, rubies have long been attributed with supernatural qualities. They were believed to possess protective powers, keeping the wearer safe from harm and warding off evil spirits. This mystical reputation has persisted through cultures and time, adding an air of enchantment to these magnificent gemstones.
Beyond their mystical significance, rubies are also associated with various healing and emotional properties. They are said to fuel passion and creativity, inspiring the wearer to pursue their dreams with fervor and courage. Rubies are also thought to enhance vitality and boost self-confidence, helping individuals tap into their inner strength and achieve greatness.
While rubies are indeed captivating in their own right, they also hold a special place in the world of fashion and romance. These alluring gemstones often steal the spotlight in exquisite pieces of jewelry, symbolizing love, passion, and commitment. Their distinctive red hue adds a touch of drama and elegance to any outfit, making them a favorite among fashion enthusiasts.
Rubies, with their fascinating scientific background and awe-inspiring beauty, remind us of the wonders that Mother Nature bestows upon us. These gems embody the perfect harmony of geological forces, chemical composition, and human creativity. So next time you encounter a ruby, take a moment to appreciate the science behind its mesmerizing charm and the magical stories it unfolds.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Facts about Rubies
1. Rubies are primarily composed of corundum, which is an aluminum oxide mineral that crystallizes in a trigonal system.
2. The red color of rubies is caused by the presence of chromium in their chemical composition. The amount of chromium determines the shade of red, from pinkish to deep red.
3. In addition to chromium, the presence of other trace elements, such as iron and titanium, can influence the color and quality of rubies.
4. Rubies are formed under intense heat and pressure, often within marble or metamorphic rocks. They are typically found in areas with a history of tectonic activity or volcanic activity.
5. The formation of rubies can take millions of years, as the necessary conditions for their creation are extremely rare.
6. Ruby crystals can form as small irregular grains or as large, well-formed hexagonal crystals. The quality and clarity of these crystals play a significant role in determining their value.
7. The hardness of rubies on the Mohs scale makes them one of the toughest gemstones, second only to diamonds. This makes them highly suitable for everyday wear in jewelry.
8. The world's largest ruby, known as the Liberty Bell Ruby, weighs an astonishing 8,500 carats and is valued at around $2 million.
9. The name "ruby" comes from the Latin word "rubeus," meaning red. In ancient Sanskrit, rubies were referred to as "ratnaraj," which translates to "king of precious stones."
10. Rubies were highly sought after by ancient civilizations and were often worn by royalty and nobles as a symbol of wealth, power, and protection.
11. The treasured "Pigeon Blood" rubies, known for their deep red color, are considered the most desirable and valuable.
12. Rubies have been used as a portable heat source. Ancient Chinese and Burmese warriors would embed rubies into their skin to provide warmth during battle.
13. According to ancient lore, rubies were believed to have protective properties that could ward off evil spirits and bring good fortune to the wearer.
14. Rubies were regarded as one of the four most precious gemstones in ancient times, alongside diamonds, emeralds, and sapphires.
15. Rubies are not only found on Earth; in 2012, scientists discovered traces of corundum, the mineral that forms rubies, on the moon. This suggests that rubies may exist on other celestial bodies as well.
Rubies are the birthstone for July.
Gem quality rubies or sapphires form in metamorphic rock like shist or gniess or igneous rock like basalt. It is possible to mine these hard rock sources but it is difficult and expensive. Luckily because these gems are so hard they weather out of relatively softer host rock. They end up in the gravel beds of streams. The high Density of the corundums cause them to be deposited in pockets. The gravel from these pockets can be sifted by hand. This is the way most rubies are mined.
In the modern era rubies can be heat treated to improve the color and clarity. This process has increased the value of otherwise low quality gems.
Location
Historically, the primary source of rubies has been Myamar (Burma). They have also been mined in Thailand, well as in Afghanistan, , India, in Madagascar, Nepal, Pakistan,In Sri Lanka, lighter shades of rubies (often "pink sapphires") are more commonly found.
Ruby Crystals for sale on fossilicious.com
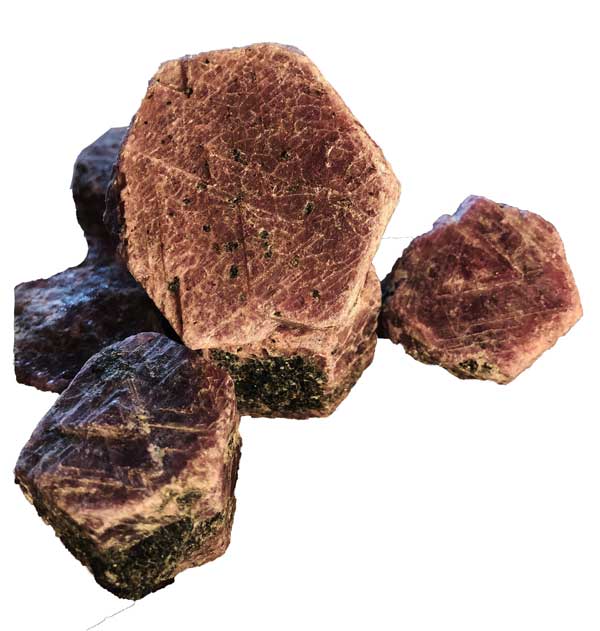

Mineral Properties of Ruby
Chemical formula: A2O3 aluminum oxide with chromium
Color(s):
light pink to deep red
Streak:
White
Luster:
vitreous to adamantine
Transparency:
transparent to opaque
Crystal system:
trigonal
Crystal Habits:
tabular hexagonal crystals.
Specific Gravity:
4.0 to 4.1
Hardness (Mohs):
9
Cleavage:
none
Fracture:
conchoidal to uneven
Uses:
Mineral Specimens, jewelry and ornamentals
Associated Minerals:
Saphire, topaz,spinel
Location:
Includes Myamar (Burma), Thailand, Afghanistan, India, Madagascar, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka,

INTERESTED IN MORE? IF SO, YOU MAY WANT TO CHECK OUT OUR OTHER SITES:
fossilicious.com - Our online fossil and mineral rock shop.
fossils-facts-and-finds.com - An educational site about fossils.